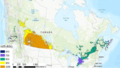
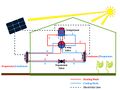
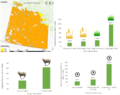
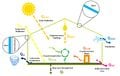
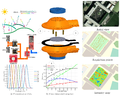
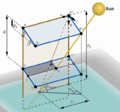
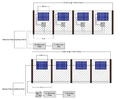
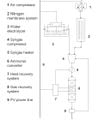
Greenhouses play a crucial role in food production and economic growth in northern regions but contribute significantly to energy consumption and carbon emissions. To address this challenge and enhance food production sustainably, there is a growing need for efficient and renewable energy solutions. Low-carbon heating in greenhouses will be achievable by using heat pumps powered by cost-effective renewable energy sources such as photovoltaic systems. This study introduces an open-source quasi-steady-state thermal model for greenhouses, non-ideal air-source heat pumps (ASHPs), and ground-source heat pumps (GSHPs) with both vertical (V) and horizontal (H) ground heat exchangers. Additionally, a ventilation sub-model is provided to manage cooling loads for residential, semi-commercial, and commercial greenhouses. Furthermore, an open-source SAM-Python-based photovoltaic system model is developed to size photovoltaic arrays for powering the heat pumps. The study reveals a nonlinear relationship between greenhouse size and annual thermal loads. It also demonstrates that ASHPs exhibit the lowest efficiency (COPh = 2.52, EERc = 9.00), followed by VGSHPs (COPh = 3.68, EERc = 19.88), with HGSHPs being the most efficient (COPh = 3.79, EERc = 19.48) for the Canadian case study. The required on-grid photovoltaic ratings to power HGSHPs, VGSHPs, and ASHPs respectively are 2.16, 2.17, and 2.64 kW for residential, 103, 104, and 128 kW for semi-commercial, and 827, 831, and 1,028 kW for commercial greenhouses. Self-consumption of designed photovoltaic systems ranges from 23.5 % to 25.1 %, with self-sufficiency varying between 23.7 % and 26.0 %. The size of the photovoltaic system is competitive with similar scenarios; however, future studies are needed to conduct an economic analysis while simulating the dynamic loads of greenhouses.
Highlights[edit | edit source]
- Heat pumps (HPs) promising solution to provide low-carbon efficient heating in greenhouses (GHs).
- Open-source quasi-steady-state greenhouse thermal model and ventilation sub-model for cooling.
- Air-source heat pump (ASHP), ground-source heat pump (GSHP).
- GSHP with both vertical (V) or horizontal (H) ground heat exchangers.
- Case study is provided for Canada to power the HGSHP, the required on-grid PV ratings for 3 sizes of GHs.
See also[edit | edit source]
The Western Innovation for Renewable Energy (WIRED) system is currently under construction to test out new open source methods to reduce PV systems costs and enable novel forms of agrivoltaics including the world's first agrivoltaic agrotunnel.

- Coal with Carbon Capture and Sequestration is not as Land Use Efficient as Solar Photovoltaic Technology for Climate Neutral Electricity Production
- Dual use of land for PV farms and agriculture literature review
- sheep
- Israeli white plastic reflectors
- A Farmer's Guide to Going Solar (NREL)
- German guidelines: https://www.ise.fraunhofer.de/content/dam/ise/en/documents/publications/studies/APV-Guideline.pdf
- 2021 review
- Miskin, C.K., Li, Y., Perna, A., Ellis, R.G., Grubbs, E.K., Bermel, P. and Agrawal, R., 2019. Sustainable co-production of food and solar power to relax land-use constraints. Nature Sustainability, 2(10), pp.972-980.
- Retrofitting solar parks for agrivoltaics
- Shading PV
- Alexis' talk at American Solar Grazing Association2021
In the News[edit source]
- Agrivoltaics: solar energy + better crops Climate and Nature
- Why solar power and farmers’ fields could be the perfect combination TVO
- Solar farms and sheep show the makings of a clean energy classic duo Business Renewables
- Agrivoltaics charge up St. Albert-area farms St Albert Gazette
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms are creating ideal growing conditions Western Wheel
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms create ideal growing conditions Voxpopuli
- 3D printed clamps for front-surface PV mounting on wood racking PV Magazine
- Harvesting the Sun to Grow in the Shade Garden Culture Magazine
- What crops fit with vertical agrivoltaics? PV Magazine
- Agrivoltaics – Keeping the farm in the solar farm Green Energy Futures
- Booming solar industry has a growing appetite for weed-chomping crews CBC
- La floreciente industria solar tiene un creciente apetito por equipos de devoradores de maleza Espanol news
- Des cochons à l’ombre des panneaux solaires, l’agrivoltaïsme gagne en popularité Radio Canada
- Pigs in the shade of solar panels, agrivoltaics gains popularity Euro Day France
- Des porcs à l’ombre des panneaux solaires, l’agrivoltaïque gagne en popularité News Day France
- ICI Radio
- The Weather Network
- Agrowoltaika zyskuje na wartości. Panele słoneczne na polu nie przekreślają upraw Business Insider Poland
- Kanada/ Coraz popularniejsza agrowoltaika: rolnictwo i produkcja energii w jednym Deon Pl
- Tu zboże, tam fotowoltaika. Rolnicy produkują i żywność i energię na jednym polu Bankier PL
- Kanada: coraz popularniejsza agrowoltaika: rolnictwo i produkcja energii w jednym MSN PL
- Agrowoltaika podbija świat (Agrovoltaics is conquering the world ) Warzywnichtow Polish
- Coraz popularniejsza agrowoltaika - rolnictwo i produkcja energii w jednym Agro Polska
- Agriculture and Energy Future - Agrivoltaics Agritecture
- MBA students examine a solar farm’s benefits for critical issues case competition Ivey
- Ontario solar curbs rankle expert BNN Bloomberg
- Kanada: coraz popularniejsza agrowoltaika: rolnictwo i produkcja energii w jednym MSN Poland