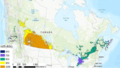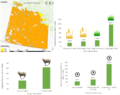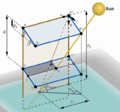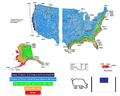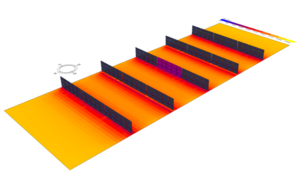
Canada can radically reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by aggressively deploying agrivoltaics and reach its goal of cutting emissions by increasing the non-emitting share of electricity generation to 90% by 2030. To help reach this goal, this study evaluated the potential energy production for vertical bi-facial solar photovoltaic arrays as well as the solar irradiation reaching the ground with three different spacings (5m, 15m and 45m) and three different Canadian farming locations (London, Calgary and Winnipeg) using irradiance modeling with Ladybug tools plug-ins for Grasshopper and Honeybee . The crops currently grown in each region were identified and their sunlight requirements were analyzed. Based on the amount of solar radiation reaching the ground surface and the solar requirements of the crops, inter-row spacings that were suitable for agrivoltaic applications for the three locations were identified. Next the land acreage of a select few crops, which were proven to be satisfactory for agrivoltaic systems, were identified for each province and their electrical energy potential was ascertained using System Advisor Model. The results indicate that more than 84% of the total national electricity requirements can be met by employing agrivoltaics on agricultural land where these crops are cultivated in the three provinces.
Highlights[edit | edit source]
- Agrivoltiac energy production for vertical bi-facial PV and solar irradiation reaching the ground
- Spacings (5m, 15m and 45m) and Canadian farming locations (London, Calgary and Winnipeg)
- Irradiance modeling with Ladybug tools plug-ins for Grasshopper and Honeybee.
- Crops currently grown in each region identified and their sunlight requirements were analyzed
- Suitable agrivoltaics + land acreage of select crops quantified = 84% Canada’s electricity needs
See also[edit | edit source]

- Coal with Carbon Capture and Sequestration is not as Land Use Efficient as Solar Photovoltaic Technology for Climate Neutral Electricity Production
- Dual use of land for PV farms and agriculture literature review
- sheep
- Israeli white plastic reflectors
- A Farmer's Guide to Going Solar (NREL)
- German guidelines: https://www.ise.fraunhofer.de/content/dam/ise/en/documents/publications/studies/APV-Guideline.pdf
- 2021 review
- Miskin, C.K., Li, Y., Perna, A., Ellis, R.G., Grubbs, E.K., Bermel, P. and Agrawal, R., 2019. Sustainable co-production of food and solar power to relax land-use constraints. Nature Sustainability, 2(10), pp.972-980.
- Retrofitting solar parks for agrivoltaics
- Shading PV
- Alexis' talk at American Solar Grazing Association2021
In the News[edit source]
- Agrivoltaics: solar energy + better crops Climate and Nature
- Why solar power and farmers’ fields could be the perfect combination TVO
- Solar farms and sheep show the makings of a clean energy classic duo Business Renewables
- Agrivoltaics charge up St. Albert-area farms St Albert Gazette
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms are creating ideal growing conditions Western Wheel
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms create ideal growing conditions Voxpopuli
- 3D printed clamps for front-surface PV mounting on wood racking PV Magazine
- Harvesting the Sun to Grow in the Shade Garden Culture Magazine
- What crops fit with vertical agrivoltaics? PV Magazine
- Agrivoltaics – Keeping the farm in the solar farm Green Energy Futures
- Solar
- Papers
- Agrivoltaics
- Solar power
- Solar energy
- Photovoltaics
- Sustainable development
- Agriculture
- SDG02 Zero hunger
- SDG07 Affordable and clean energy
- SDG08 Decent work and economic growth
- SDG09 Industry innovation and infrastructure
- SDG12 Responsible consumption and production
- Canada
- Energy policy
- Farming
- Energy
- Land use
- FAST Completed