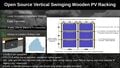
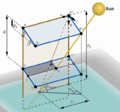
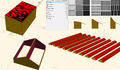
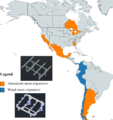
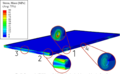
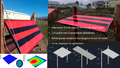
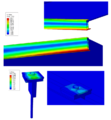
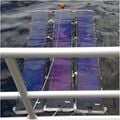
The prohibitive costs of small-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) racks decrease PV adoption velocity. To overcome these costs challenges, an open hardware design method is used to develop two novel variable tilt racking designs. These are the first stilt-mounted racking designs that allow for the manual change of the tilt angle from zero to 90 degrees by varying the length of cables. The racks are designed using the calculated dead, wind, and snow loads for Canada as a conservative design for most of the rest of the world. Structural capacities of the wooden members are then ascertained and the resisting bending moment, shear force, tensile force, and compressive force is calculated for them. A structural and truss analysis is performed to ensure that the racking design withstands the applicable forces. Moreover, the implications of changing the tilt angle on the wooden members/cables used to build the system are also determined. The systems offer significant economic savings ranging from one third to two thirds of the capital expenses of the commercially available alternatives. In addition, the racking designs are easy-to-build and require minimal manufacturing operations, which increases their accessibility. The stilt-mounted designs can be employed for agrivoltaic settings while allowing farm workers shaded, ergonomic access to perform planting, weeding, and harvesting.
Source
- Jamil, U.; Vandewetering, N.; Sadat, S.A.; Pearce, J.M. Wood- and Cable-Based Variable Tilt Stilt-Mounted Solar Photovoltaic Racking System. Designs 2024, 8, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8010006 preprint

Keywords[edit | edit source]
Sustainable development; Open-source; Photovoltaic; Racking; racking; solar energy; biomaterials; wood; photovoltaic; mechanical design; balance of systems; renewable energy
See also[edit | edit source]
- To Catch the Sun
- 3-D printable photovoltaic module spacer
- Open source DIY solar photovoltaic racking
- Circular PV panel
Open Source Photovoltaic Racking Approaches[edit source]
- Ground-mounted
- Roof-mounted
- FPV