Rope pumps
Industrial hand pumps, such as the Indian Mark II, for communal wells donated by development projects often break down after two years. If maintenance costs are the responsibility of the users, then this cost is too high when repairs prove necessary and the pump is left nonfunctional.
An alternative reliable hand pump is needed for communal and private use to supply clean drinking water and irrigation. These pumps will raise the standard of living if they are low cost, reliable and pump water effectively. Efficiency is critical to irrigate a garden in the dry season due to the relatively large amount of water involved. Such gardens provide food and increased income.
Local affordability, maintenance and good pump efficiency are required features. Local affordability means a twenty-to-hundred-fold cost reduction compared to imported industrial goods. Local maintenance is only possible when made with local resources and skills.
The pumping system should prevent contamination of drinking water by permitting the well to be sealed. This is especially true of communal wells. Industrial pumps need to be bolted onto a concrete slab positioned over the well. However, this makes the water inaccessible when the pump breaks down. Immediate maintenance on the pump or access to the well through an emergency hatch permits continuous access to life-giving water.
How[edit | edit source]
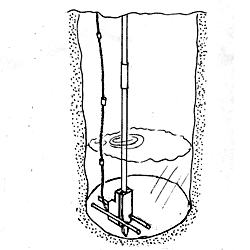
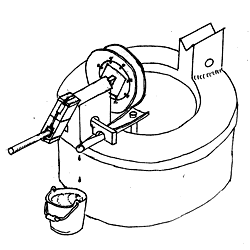
- Low cost modern materials as plastic pipe and rope are used in a rotating hand pump system. The rope pump works on the principle of the chain pump with the chain replaced by rope and the rotating chain drum by a specially constructed rubber disk wheel. Such a rubber wheel can be made from used car tires. Other needed materials can be found at little or no cost.
- Little time is needed to instruct users or craftsman to construct a rope pump. People adapt the basic principle to their own needs, whether shallow or deep wells, whether wells have boreholes, or horizontal pumping from a pond. To achieve quality, instruction should emphasize the importance of the relationship between wheel diameter and the diameter of the plastic pump pipe. Additionally the correct construction of the place where the rope movement changes direction from downwards to upwards in the bottom of the well is crucial.
- If instructions regarding quality are followed, the rope pump outclasses the traditional pump by far. The Demotech Rope-pump is superior in all aspects of use, as well as price per unit, when compared to other types of hand-pumps.
- Further development could mean cutting the cost-price per unit in half, making it suitable for 100m holes, quick and efficient maintenance, robust construction and housing, as well as more-efficient propulsion and higher efficiency.
- The rope pump can be adapted for special situations. To make it suitable for being mounted on a well cover the bearing of the pump axle is positioned at one side of the pump wheel only. In most other set-ups it is preferred to have the bearing on both sides of the pump wheel.
Knots[edit | edit source]

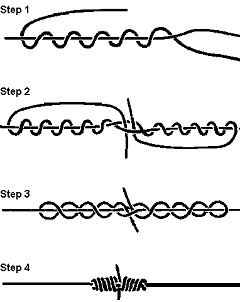
The 'washers' on the rope pump need to be made from a material that is cheap and easily available. They also need to be easily repairable or replaceable. This is necessary when washers crack off or wear over time. Another priority is to have the 'washers' made from a material and in such a way that their construction and repair can and will be done by women. This is because it is usually the women's task to collect water, and so the water pumps will be mainly used by women. The design of the 'washer' should therefore be a design that is 'appropriate for women'. The 'washer' should fit into the pump pipe loosely, it needs to be securely attached to the pump rope and it needs to have a system of construction that is simple and easy to explain and learn.
To make rope elements, one to two meters long and ending in a knot that loosely fits the pipe is an alternative for rubber or plastic washers slid over the pump rope or knots made at intervals in the pump rope. It would be women's work to make such rope elements in a handicraft way like Macramé. When hauling water, women can keep track of the wear of such rope elements and replace one element when necessary. This replacement can be done in a few minutes, there is no need to take the pump out of service. The picture shows a complex piece of macrame work. In a similar way the rope element should be made: thin rope, woven into a sting, a loop at one end and a thick knot at the other end. Each loop can be attached to the knot of the next rope element by inserting it into an opening in the knot. There the loop can be fastened.