Hybrid fuel cell
Fuel cells are emerging as an attractive power supply source for applications such as distributed generation power systems
and electrical vehicles. Hybrid fuel cell technology can be applied to various fields: electricity power plants, automotive manufacturing,
cogeneration, smartphone, construction and etc. Hybrid fuel cells has the following advantages: cleanness, high efficiency and high
reliability. Fuel cells operate without the efficiency limitation of the Carnot cycle and without the pollution associated withe the combustion
of fossil fuels.[1] However, there are also disadvantages: it cannot store energy, the response is slow, difficult to cold start
and its output voltage fluctuates with the load.[2]
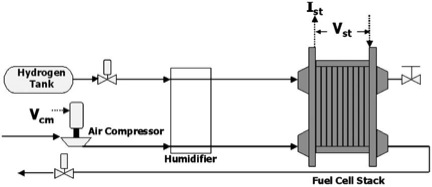
Simple fuel cell and air compressor power system.
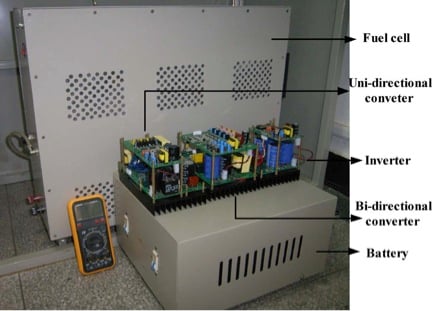
Photograph of the hybrid fuel cell power system.
Types Fuel Cells[edit | edit source]
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell
Electricity, water and heat can be produced when hydrogen and oxygen combined as a fuel cell. If compared to batteries
which has limited lifespan, the fuel cell will produce electricity as long as the fuel (hydrogen) is supplied, and nver losing its charge.[3]
- Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM)
Polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cells employ a polymer membrane with acid side groups to conduct protons from the
anode to cathode. Water management in the fuel cell is critical for PEM fuel cell operation. Sufficient water must be absorbed into
the membrane to ionize the acid groups; excess water can flood the cathode of the fuel cell diminishing fuel cell performance
limiting the power output.[4]
See Youtube video of How PEM Fuel Cell works.
- Direct Methanol Fuel Cell
- Alkaline Fuel Cells
- Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells
- Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cell
- Regenerative Fuel Cell
For comparison of fuel cells, see here[5]
Hybrid Fuel Cell Power System Models[edit | edit source]
- Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR),[6] see also Continuous stirred-tank reactorW at Wikipedia.
- Compressor Model[7]
A Sample Hybrid Fuel Cell Power System[edit | edit source]
Components of a Hybrid Fuel Cell Power System[edit | edit source]
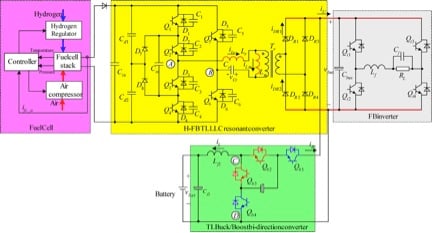
- Full Cell
- Unidirectional Converter
- Bidirectional Converter
- Battery
- Inverter
Main circuit of whole system
Operation Principle[edit | edit source]
- Cold Start
- Overload
Power Management[edit | edit source]
- Operation Conditions of the Battery
- Operation Conditions of the Fuel Cell
- Power Flow of the Power System
- Slip-In Point and Slip-Out Point
Implementation of Control Circuit[edit | edit source]
- Unidirectional Converter Control
- Bidirectional Converter Control
- Power Management Control
(Note: for the complete design and analysis of this proposed sample hybrid fuel cell power system, please read A Hybrid Fuel Cell Power System by Jin et al.[8])
Applications[edit | edit source]
- Hybrid vehicles
- Clean Power Generation, see article Hybrid Fuel-Cell Strategies for Clean Power Generation.[9]
See how hydrogen fuel cells applied to aircraft:
Challenges of Hybrid Fuel Cell Technology[edit | edit source]
- Cost
- Durability and Reliability
- System Size
- Air, Thermal and Water Management
- Improved Heat Recovery Systems
Please read Fuel Cell Technology Challenges.[10]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ A. Dalvi and M. Guay. 2009. Control and Real-time Optimization of an Automotive Hybrid Fuel Cell Power System. Control EngineeringPractice17(2009)924–938.
- ↑ Jin, K et al. 2009. A Hybrid Fuel Cell Power System. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. VOL.56, NO.4.
- ↑ Hydrogen Energy. http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/tech/hydrogen
- ↑ http://www.princeton.edu/~benziger/PEMFC.pdf
- ↑ http://www1.eere.energy.gov/hydrogenandfuelcells/fuelcells/fc_types.html
- ↑ http://web.archive.org/web/20120629030116/http://www.engin.umich.edu:80/~cre/asyLearn/bits/cstr/
- ↑ Pukrushpan, J.T.,Peng,H., and Stefanopoulou,A.G.(2004). Control of Fuel Cell Power Systems.
- ↑ Jin, K et al. 2009. A Hybrid Fuel Cell Power System. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. VOL.56, NO.4. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/Xplore/login.jsp?url=http%3A%2F%2Fieeexplore.ieee.org%2Fstamp%2Fstamp.jsp%3Ftp%3D%26arnumber%3D4668419&authDecision=-203
- ↑ Rajashekara, K. 2005. Hybrid Fuel-Cell Strategies for Clean Power Generation. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, VOL. 41, NO. 3, MAY/JUNE 2005. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/freeabs_all.jsp?arnumber=1432990
- ↑ Fuel Cell Technology Challenges, http://www1.eere.energy.gov/hydrogenandfuelcells/fuelcells/fc_challenges.html