A heat engine, such as the Stirling engine, typically uses energy provided in the form of heat to do work and then exhausts the heat which cannot be used to do work. They operate in a cyclic manner and are usually illustrated by a PV diagram.
A heat pump can be considered to be a "heat engine in reverse", in which energy is applied to transfer heat into or out of an area as desired.
Stirling engine
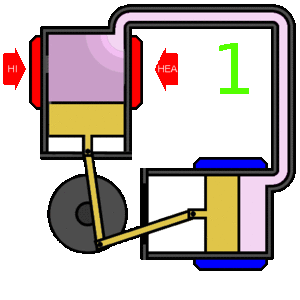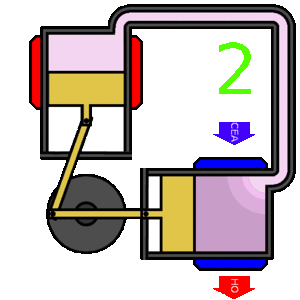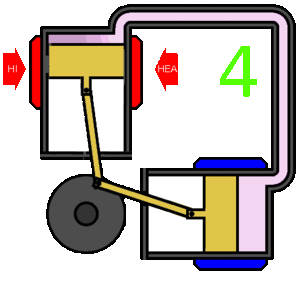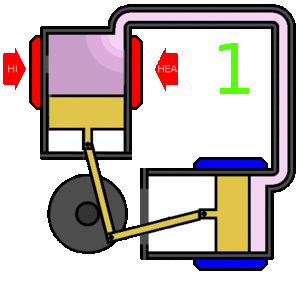
The Stirling engine is a type of heat engine. In simple terms, the Stirling works by very efficiently converting heat energy to mechanical energy. It is considered to be one of the most efficient types of engine.
Any source of heat can be used for a Stirling engine, including solar, waste heat, or burning various fuels. Stirling engines are typically larger than internal combustion engines (or to put it another way, a Stirling engine typically produces less power than a similarly-sized internal combustion engine), limiting use in vehicles.
External links
- Wikipedia:Heat engine
- This site provides a concept map that explains heat engines.